Engineering a Better Racking System
20 July 2018
'All Pallet Racking is the same.' This common misconception continues to appear as customers turn to price before engineering and quality when making purchasing decisions. Is that a safe choice?

It is important to realise three main points when it comes to fitting out your warehouse:
- Not all pallet racking is engineered and tested to suit your requirements.
- Not all pallet racking complies to AS4084:2012.
- Not all pallet racking is the same.
Hazard or Bargain?
So how do you figure out the difference between a bargain and a hazard? Sadly it is never as easy as staring questionably at the product, instead, we advise you ask a company to show you their engineering and testing process to remove any doubts about their product and prove they comply to AS4084:2012.
If the results prove that you are comparing products that have been engineered to the same specification and both comply, then you have a bargain! If not, you're now comparing two different systems.
Who are we?
APC have been designing, engineering and manufacturing pallet racking in Perth, Western Australia for over 45 years. This process is exhaustive and complex to ensure we provide our customers with the most flexible, cost effective and safe designs. We also have a full time in house research and development team which are continually analysing and physically testing racking components. This is done so we can accurately predict the behaviour of our racking through different conditions and compare it against our racking analysis software results to ensure it complies and can be certified to AS4084:2012, the Steel Storage Racking Australian Standard.
APC's Process of Certification
APC have a twelve (12) stage process of certification as follows;
- Moment Rotation Characteristics of Beam/Upright Connection
- Frame Shear Flexibility
- Pallet Beam in Upright Frame Assembly Test
- Stub Column Test
- Coupon Test
- Moment Rotation Characteristics of Beam/Upright Connection
- Finite Strip Analysis
- Geometric Non-Linear Analysis
- Member Capacity Checks
- Installation
- Rack Certification
- Operation and Maintenance
1. Moment Rotation Characteristics of Beam/Upright Connection
All beams undergo Portal Tests and Cantilever Tests with all models of racking upright to determine the interaction between each combination. The Portal test is used to determine the stiffness of the semi-rigid joints, while the Cantilever test is used to determine the strength of the joints.
2. Frame Shear Flexibility
Shear tests are used to determine the transverse shear stiffness of the upright frame so we can accurately predict the cross aisle deflection. Using the full stiffness of the frame would mean the deflection is grossly underestimated resulting in a very unstable rack. (AS4084:2012 states that in lieu of testing the axial stiffness of the bracing should be reduced to 5%)
3. Pallet Beam in Upright Frame Assembly Test
APC Engineering also go further than required by AS4084:2012 and perform testing that was present in AS4084:1993 but removed during the revision to the 2012
version. The Pallet Beam in Upright Frame Assembly test which simulates the conditions of the rack in service. This test double checks that the calculated theoretical loads using the information above, corresponds to the deflection present under that load.
4. Stub Column Testing
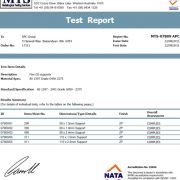
NATA certified laboratories conduct stub column tests on all models of upright. The Stub Column test is a compression test on a short length of upright to destruction, so the effects of the perforations along the uprights and the section capacity can be determined.
5. Coupon Testing
NATA certified laboratories also conduct coupon tests on tested samples to determine the actual yield strength of the material so results can be normalised against standard supply of material.
6. Moment Rotation Characteristics of the Floor Connection
APC supplies samples to Dr Moll in Germany, one of the world’s leading authorities in pallet rack testing. Where all
combinations of APC footplate, baseplate and upright types are assembled and anchored to the floor for testing to determine the moment-rotation characteristics of the floor connection.
7. Finite Strip Analysis
Testing however is just the start in determining the capacity of a racking system, each section, beam, upright and brace must have its section properties determined. At APC we use finite strip analysis, an offshoot of finite element analysis, to determine the section properties.
Once we have the gross section properties, each must be examined against the requirements of AS4600:2005 Cold Formed Steel Structures, to check what elements of the section have reached the yield strength and therefore reduce the overall effectiveness of the section. These effective section properties are then used in the racking analysis.
8. Geometric Non-Linear Analysis
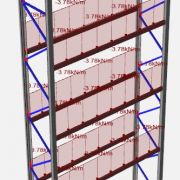
Once we have all the Effective Section properties and connection stiffness’s the racking structure can be modelled in the Structural Analysis Program. This model is where the critical application of AS4084:2012 commences. Each required action and action combination must be applied and racking imperfections accounted for.
The model of the rack structure then undergoes a geometric non-linear analysis to determine the critical action effects and an equilibrium must be obtained in the deformed frame configuration, a sway bucking analysis is performed to ensure the racking frames do not buckle prior to the full load being applied.
9. Member Capacity Check
Once the action effects are determined, each racking member must have its capacity checked against these action effects to ensure they are not overloaded. This capacity is checked through the requirements of AS4600:2005 with some modifications from AS4084:2012 and if all members have sufficient capacity the engineering is deemed acceptable.
10. Installation
With the engineering complete, we still cannot say that the racking conforms to AS4084:2012, we still have to confirm that the racking is installed correctly before the racking installation can be deemed to conform.
Incorrectly installed pallet racking can affect the structural integrity of the system. It is critical that suppliers of pallet racking ensure their racking is installed to AS4084:2012 tolerances and requirements.
11. Rack Certification
Once the pallet racking has been installed correctly with the appropriate load signage, the rack certification can be issued for the project in question.
12. Operation and Maintenance
AS4084:2012 states that the racking supplier is required to provide user manuals and appropriate training to the end user for correct use and maintenance of the racking to ensure the safety of the equipment is maintained. Regular inspections are vital in identifying damage which must be repaired to retain the safety and structural integrity of the pallet racking. The client must understand the safety of the operators is paramount and the onus is on the client to ensure the racking is annually inspected and repaired if required.
It is also important to stress to the client that changing the height of the beams can reduce the capacity of the racking and therefore potentially overload it and therefore placing employees at risk. The client should consult the racking supplier prior to making any changes.